Does Alternator Charge Car Battery?
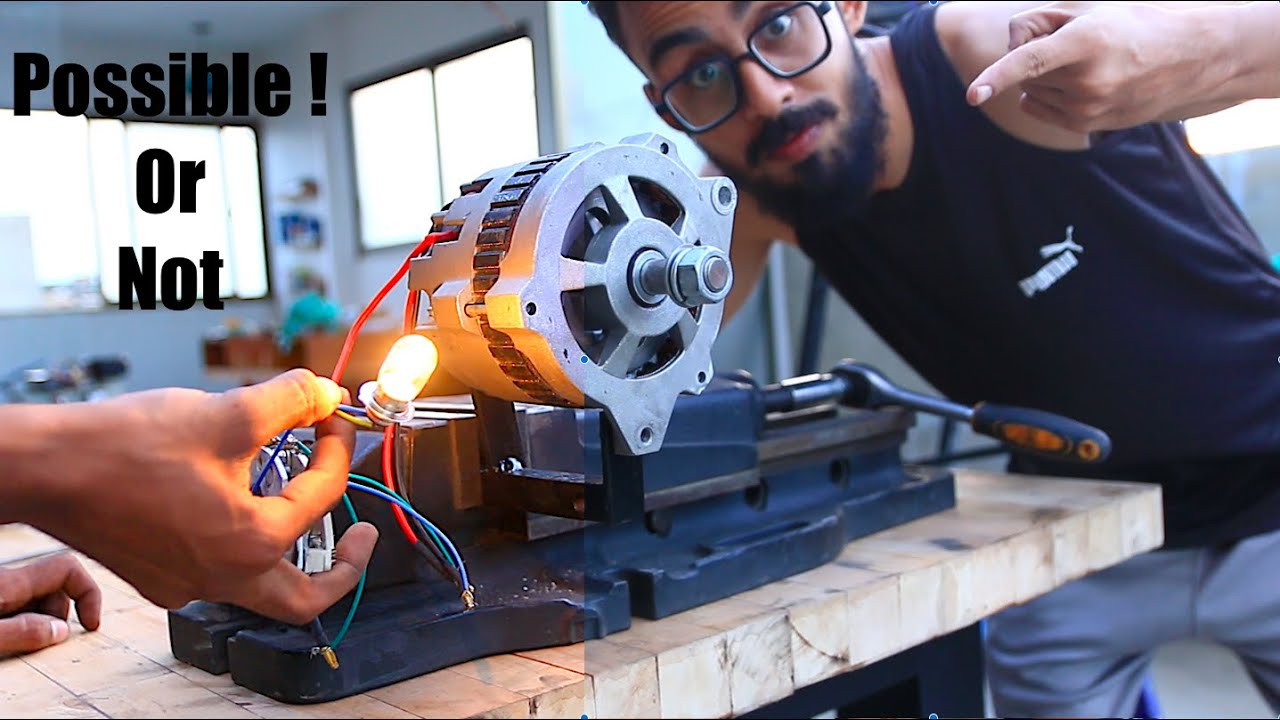
A common question many drivers ask is, “Does the alternator charge the car battery?” The short answer is yes. The alternator plays a vital role in the electrical system of your car, ensuring the battery stays charged and that all electrical components run smoothly. In this blog post, we’ll explore how the alternator charges the car battery, what happens when it fails, and how to keep your battery and alternator in top condition.
How Does the Alternator Work?
The alternator is a key component of your car’s charging system. Here’s how it operates:
- Power Generation
- The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine into electrical energy using a belt-driven system.
- Inside the alternator, a rotor spins within a stator, generating alternating current (AC). This current is then converted to direct current (DC), which is used to charge the battery.
- Battery Charging
- When the engine is running, the alternator supplies electrical power to the car and recharges the battery simultaneously. It ensures the battery has enough power to start the engine the next time you turn the key.
- Maintaining Electrical Systems
- In addition to charging the battery, the alternator powers the vehicle’s electrical systems, such as lights, radio, and air conditioning, while the engine is running.
Signs That the Alternator Is Charging the Battery
Under normal conditions, the alternator continuously charges the battery while the engine is running. Here are signs that your alternator is working properly:
- Stable Voltage Levels
- A fully functional alternator maintains the battery voltage between 13.7 and 14.7 volts while the engine is running.
- No Warning Lights
- Modern vehicles have dashboard indicators that light up if the alternator or battery isn’t functioning correctly.
- No Starting Issues
- If your car starts easily without hesitation, it’s a sign that the alternator has been keeping the battery charged.
What Happens When the Alternator Fails?
When the alternator stops functioning, the battery cannot recharge, leading to a range of issues:
- Battery Drains Quickly
- The car will rely solely on the battery for power. As a result, the battery may drain completely after a short time.
- Electrical Failures
- Lights may dim, the radio might cut out, and other electrical systems can fail due to insufficient power.
- Engine Stalls
- A dead battery caused by a failed alternator can lead to engine stalling, leaving you stranded.
How to Check if the Alternator Is Charging the Battery
You can perform a few simple tests to verify whether your alternator is charging the battery:
- Check the Voltage
- Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage with the engine off and running.
- A reading of around 12.6 volts with the engine off indicates a healthy battery.
- When the engine is running, the voltage should rise to 13.7–14.7 volts.
- Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage with the engine off and running.
- Inspect the Alternator Belt
- Ensure the belt driving the alternator is tight and free of cracks or wear. A loose or damaged belt can prevent the alternator from charging effectively.
- Dashboard Warning Light
- Most vehicles have a battery or charging system warning light. If this light stays on while driving, it’s a sign of a potential alternator issue.
FAQs
1. How long does it take for an alternator to charge a dead battery?
- It depends on the alternator’s output and the battery’s capacity. Typically, a healthy alternator can charge a dead battery in about 30 minutes to an hour of driving.
2. Can a car run without an alternator?
- A car can run briefly without an alternator, but it will rely solely on the battery for power, which will deplete quickly.
3. Can an alternator overcharge the battery?
- Yes, a faulty alternator can overcharge the battery, causing damage. Overcharging often results from a malfunctioning voltage regulator.
4. Does revving the engine charge the battery faster?
- Yes, increasing engine RPM can help the alternator generate more power, charging the battery faster. However, this should not be a regular practice.
5. What can damage the alternator?
- Common causes of alternator damage include worn-out belts, electrical overloads, and exposure to extreme heat or moisture.
Tips to Prolong Alternator and Battery Life
- Regular Maintenance
- Inspect and replace the alternator belt if it shows signs of wear.
- Avoid Overloading Electrical Systems
- Minimize the use of high-demand electronics (like the AC and headlights) when the engine is idling.
- Keep the Battery Clean
- Corrosion on battery terminals can interfere with the alternator’s ability to charge the battery efficiently.
- Test the System Periodically
- Have your car’s charging system checked during routine maintenance to catch any issues early.
Conclusion
The alternator is essential for keeping your car battery charged and ensuring all electrical systems function properly. Without it, the battery would quickly drain, leaving your car unable to start. Regular maintenance and monitoring can help ensure that your alternator and battery remain in good condition. If you notice any signs of alternator failure, it’s best to address the issue promptly to avoid being stranded on the road.
Also Check:
• Does Your Alternator Charge Your Battery?
• Does the Alternator Charge the Battery?
• Does a Bad Alternator Kill a Battery?






2 Comments